What is RFID?
To those first looking at radio frequency identification (RFID) and its possible applications, I would like to start with an RFID definition and present an overview on how RFID works.
RFID is an applied technology that is used to discover and record the presence of a tagged object using radio signals. Common RFID applications include inventory control, asset management, theft prevention, and such new areas as the timing of running events and keeping track of students in schools. Many new applications involving RFID are currently being developed to exploit this technology.
Some of the advantages of RFID technology include the ability to uniquely identify individual items, locate items that are not in direct line-of-sight, and to recognize many tagged items concurrently.
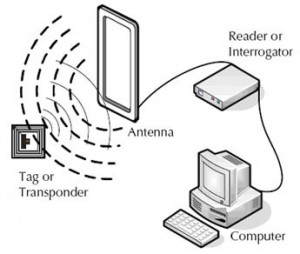
RFID applications are implemented as an ecosystem of core components of hardware and software. The RFID ecosystem includes the tags that identify what is being recognized, the readers and antennas that are used to discover and communicate with the tagged items, and the software that controls the readers and acts as middleware to store the tag information and provide input to the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems as required.
To create the RFID application means deploying an RFID system of tags, antennas, readers, and software. Typically, installing a system requires basic hardware-including attaching the tags in their proper places, powering the readers and reader antennas-as well as running the reader control and application software.
Unless the customer is experienced in these matters, system integrators can help to set the system up and perform testing. When all of these components come together, the RFID applications can be effectively and efficiently deployed. RFID system applications can help improve the quality of business operations and the inventory and customer experience in a variety of ways for any number of vertical markets and industries.
With RFID applications in place, an enterprise has the ability to decrease reliance on manual processes, increase the efficiency and effectiveness of operations, improve asset inventory and traceability, reduce overall operations costs, and provide useful data for business analytics to improve enterprise processes and work flows. RFID is a proven technology that scales for future growth in many directions. Can you imagine a new “killer app” for your business application area that could use RFID technology?